გრაფიკი, რომელიც სასარგებლოა იმ თვალსაზრისით, რომ გვეხმარება (შესაბამისი ალბათობების ჩართვით) უკეთესად გავერკვეთ ისეთ სიტუაციაში, როცა თანმიმდევრულად ხდება რამოდენიმე მოვლენა.
მაგალითი: ვთქვათ, 120 ადამიანიდან ერთი არის დაავადებული რაღაც დაავადებით. ადამიანებს უტარდებათ ტესტირება ამ დაავადებაზე. ბევრი სამედიცინო ტესტი არ არის სრულყოფილი და ზუსტი. ვიგულისხმოთ რომ, როცა ტესტირება უტარდება ადამიანს, რომელსაც აქვს დაავადება, მაშინ 0.9 ალბათობით მიიღება სწორი დადებითი შედეგი „+“ ანუ ტესტირება აღმოაჩენს არსებულ დაავადებას. ჯანმრთელ ადამიანებში სწორი უარყოფითი შედეგის „-“ მიღება ხდება ტესტების 80%-ში. დენდოგრამის დახმარებით დავთვალოთ ალბათობა იმისა, რომ:
1. თუ ადამიანი ჯანმრთელია, მისი ტესტი იქნება დადებითი „+“ (დაავადებულია).
2. შემთხევით შერჩეული ადამიანი ჯანმრთელია და მისი ტესტირების შედეგია „+“.
3. შემთხვევით შერჩეული ადამიანის ტესტირების შედეგი იქნება „+“.
4. შემთხვევით შერჩეული ადამიანის ტესტირების შედეგი იქნება „-“ (ჯანმრთელია).
***
გამოყენებული ლიტერატურა:
Field, A. (2013). Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics. SAGE Publications Ltd.
კისი, ჰ. (2008). სტატისტიკა სოციალურ მეცნიერებებში. სოციალურ მეცნიერებათა ცენტრი. თბილისის უნივერსიტეტის გამომცემლობა
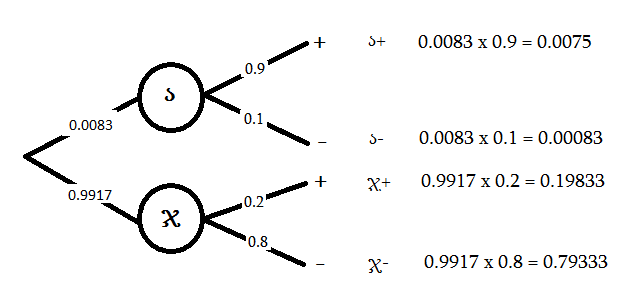
შემოვიღოთ აღვნიშნები:
„ა“ - ადამიანი დაავადებულია, P( ა) = 1/120 = 0.0083.
„ჯ“ - ადამიანი ჯანმრთელია, P(ჯ) = 1-0.0083 = 0.9917
მოცემულობის თანახმად, თუ ადამიანი ავადაა, ტესტი დადებით სწორ შედეგს აჩვენებს 90% ცდაში ანუ P( + თუ „ა“) = 0.9.
თუ ადამიანი ჯანმრთელია, ტესტი ადასტურებს ამას 80% ცდაში ანუ
P (- თუ „ჯ“) = 0.8.
დიაგრამიდან ჩანს, რომ
P(- თუ „ა“) = 1-0.9 = 0.1 და P (+ თუ „ჯ“) = 1-0.8 = 0.2
შემდეგი ხდომილობების ალბათობებს პოულობენ ზემოთ მოცემული ხისებრი დიაგრამიდან შესაბამის შტოებზე აღნიშნული ალბათობების გადამრავლებით:
P(ა და +) = P(ა +) = 0.0083 × 0.9 = 0.0075.
P(ა და -) = P(ა -) = 0.0083 ×0.1 = 0.00083.
P(ჯ და +) = P(ჯ +) = 0.9917× 0.2 = 0.19833.
P(ჯ და -) = P(ჯ -)=0.09917× 0.8 = 0.793.
დიაგრამიდან ასევე ვიპოვით 1, 2, 3, 4 კითხვების პასუხებს:
1. P(თუ ადამიანი ჯანმრთელია, მისი ტესტი +) = 0.2.
2. P(ადამიანი ჯანმრთელია და მისი ტესტი +) =P(ჯ და +)=0.9917× 0.2 = 0.19833.
3. P(+) = P(ა+ ან ჯ+) = 0.0075+ 0.19833 = 0.20583.
4. P(-) = P(ა-)+P(ჯ-) = 0.00083+0.793 = 0.7942.
